

Did you know the air compressor, an ordinary tool in most garages, is responsible for some of the most advanced technological feats of our time? Yes, even the Mars Rover relies on this unassuming device—proving that it's more crucial than ever.
In a time where efficiency and sustainability drive innovation, understanding air compressors can drastically alter both industrial processes and daily life. With energy costs skyrocketing, the potential savings and versatility offered by this tool are game-changers.
Air compressors aren't just about filling up tires anymore. They're pivotal in powering complex machinery in manufacturing and even play a role in preserving our environment. Yet, not many people are aware of the surprising ways these tools are used outside of conventional settings. Did you know that air compressors are used in cutting-edge medical tech, enabling life-saving devices to operate smoothly? But that’s not even the wildest part…
In your very home, air compressors can multiply your labor efficiency tenfold. Whether you're inflating a pool or powering a paint sprayer, this tool reduces time while increasing output spectacularly. And while these benefits might seem unbelievable, the full capabilities of air compressors are just beginning to surface. What happens next shocked even the experts…
In industrial settings, air compressors serve as the unsung heroes of productivity. They amplify the power behind assembly lines and play a crucial role in food packaging. Filled with capabilities that extend far beyond air production, they facilitate the automation that transforms raw materials into products with speed and precision. But there’s one more twist to their industrial prowess: they’re also instrumental in reducing waste and improving sustainability, which aligns with modern green initiatives.
Air compressors also help maximize resource efficiency by enabling equipment like pressurized pneumatic pumps that minimize product loss. This effective conservation stems from their unmatched compressive abilities, which also enhance recycling processes within factories. Yet, despite their widespread industrial use, many outside these environments remain unaware. Perhaps the most startling fact is how these compressors contribute significantly to innovation in high-tech industries, such as electronics manufacturing. What you read next might change how you see this forever.
One might ask, how do factories keep up with ever-increasing production demands without compromising on quality? The answer is simple yet profound: by optimizing their equipment with top-tier air compressors. Units from reputed brands ensure not only performance but longevity, contributing to less downtime and higher productivity. These devices are constantly upgraded to offer smarter, more intuitive control systems, further proving their indispensable value. But even this is just scratching the surface...
Furthermore, air compressors’ ability to harness energy efficiently positions them as a prime tool for future-proof operations. Companies increasingly see the utility bills shrink and their carbon footprint diminish, painting a brighter picture of sustainable industry. In upcoming pages, we'll delve into unexpected applications that redefine air compressors’ perceived limitations. Brace yourself, because the implications are broader than you could ever imagine.
The shift from industrial to personal use opens a plethora of surprising advantages for homeowners. With air compressors, you can easily accomplish tasks that typically demand multiple tools. Whether you’re nailing wood, painting walls, or inflating sport equipment, these devices make home projects significantly more manageable. They can turn a cluttered garage into a lean DIY powerhouse, optimizing every square inch with their versatile usage. But get ready for the twists yet to come...
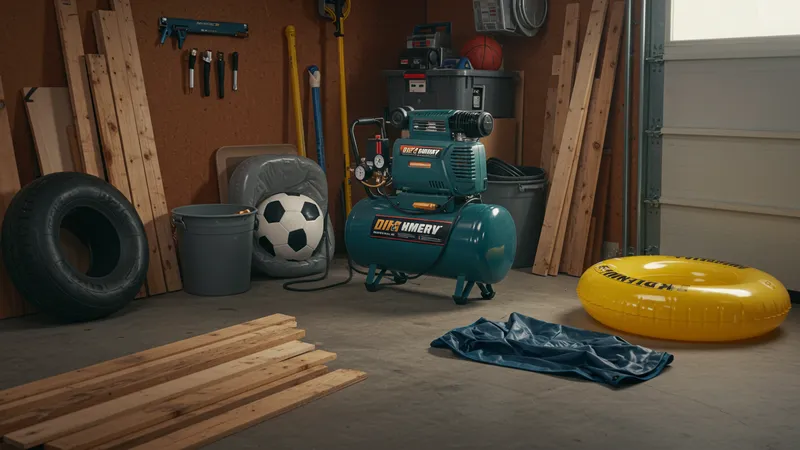

Home projects have never been simpler or more efficient. Air compressors replace or enhance the functionality of various household tools, offering a cost-effective, time-saving alternative. Instead of buying multiple specialized tools, one can invest in a single air compressor to handle a variety of tasks. The sheer variety of accessories allows one to explore DIY possibilities previously thought too burdensome. Consider the convenience of switching from sanding to cleaning in minutes with the right attachments. However, the most intriguing aspect might just blow your mind.
Curious about their impact on your home renovation budget? Air compressors dramatically cut down on rental costs for equipment. Having a reliable compressor ensures that so many DIY tasks transition from daunting to doable, changing the mindset of homeowners about limitations. These days, being handy is not just about talent; it’s also about having the right tools — particularly the multi-faceted compressor. Discovering more will surely spark your interest to explore further.
When planning home upgrades, the unpredictability of costs can be daunting. But this narrative shifts when air compressors enter the picture. The ease of using pneumatic tools, often delivering faster completion times and reduced physical exertion, exemplifies their often underestimated importance. It's time we delve into the nitty-gritty of these game-changing devices and assess their true impact on home improvement strategies. The revelations up next are beyond belief!
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability, air compressors contribute unseen but impactful strides in environmental conservation. These tools reduce waste by improving the efficiency of energy use across various industries, helping decrease carbon emissions. This makes them vital players in achieving a greener planet, especially when paired with renewable energy sources. The significance of these contributions cannot be understated; they effectively aid in the global battle against pollution. Discoveries in this realm will truly astound you.
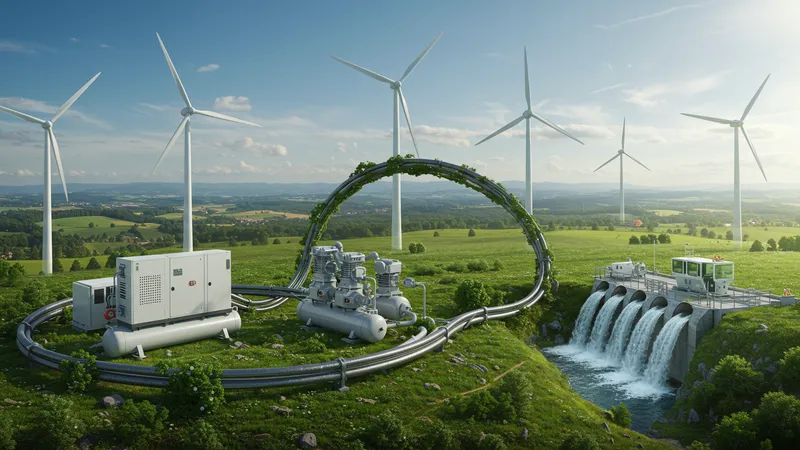

Notably, air compressors have been integral in developing innovations in green technology. They assist in the operation of wind turbines and hydroelectric systems, maximizing resource capture and distribution. Such partnerships between compressors and renewable energy forms present an eye-opening example of versatile mechanical teamwork fundamentally shaping eco-friendly futures. However, it's what's hidden beneath these synergistic roles that’s more fascinating.
The logistical capabilities of air compressors also mean there's reduced dependency on chemical production processes that require toxic solvents. Instead, energy-efficient compressors leverage air, a clean medium, to perform functions traditionally reliant on hazardous compounds. This surprisingly effective substitution marks a shift towards non-toxic manufacturing, placing air compressors as central components in the clean tech evolution. But there’s more to the story still waiting to be uncovered.
As air compressors advance, their environmental benefits grow. Through optimizing energy consumption frameworks and supporting more sustainable manufacturing practices, they catalyze a transformative movement towards minimizing industrial environmental impact—without compromising performance. The implications of such advancements become significant when gauged against a backdrop of global environmental challenges. Unravel the evolving narrative and learn how innovation leverages these devices for climate action.
In the realm of healthcare, air compressors are revolutionizing medical technology in ways few would expect. From powering respiratory devices to maintaining precise airflows in complex surgeries, these tools are vital to modern medicine. Their technological precision and reliability ensure life-saving equipment operates efficiently and safely. Yet their true breadth within the medical field is only beginning to be known. Stay tuned for breakthrough details…
Let’s unveil the latent power of air compressors in hospitals and clinics. They support ventilators, which became especially crucial during the recent pandemic, underscoring their undeniable importance. With their capability to provide precise pressure and airflow, compressors enable intricate medical procedures that demand exacting conditions. Advancements in this area raise the bar for healthcare standards globally, and the continuing developments promise even more profound implications.
Beyond immediate healthcare applications, air compressors contribute to pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring sterile and contamination-free environments. They are integral to processes like oxygen production and various forms of sterilization, positioning them as significant threads in the web of global health. As we expand this conversation, prepare to encounter revelations that highlight their critical role in innovative health solutions.
As healthcare continues its rapid progression, the demand for resilient, high-performance compressors grows. Engineers and medical professionals consistently collaborate to enhance these tools, ensuring they meet rigorous health compliance standards. This partnership promises a frontier of medical possibilities that harness compressor technology in unprecedented ways, changing the narrative about what’s achievable in healthcare. The secrets to be disclosed are nothing short of extraordinary.
Beyond static industry uses, air compressors maintain and transform transportation as well. These devices power pneumatic systems in public transport, ensuring smooth and safe passenger journeys. From trains to airplanes, air compressors facilitate critical functions that keep these services running efficiently. There's a fascinating layer of complexity to their roles here, hiding impactful insights.
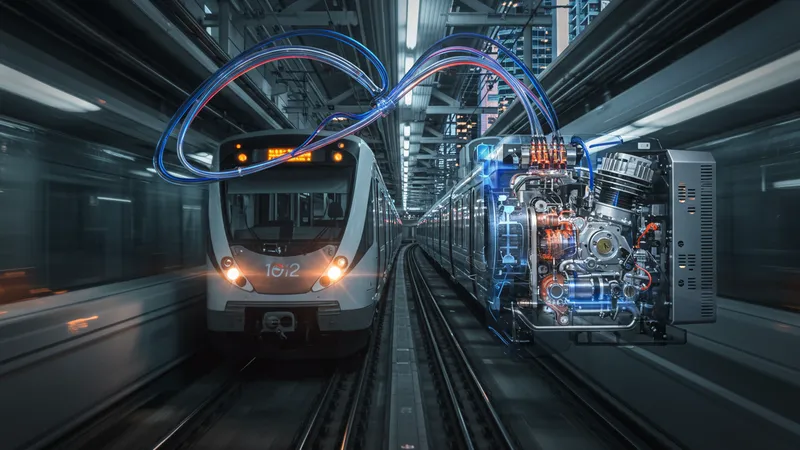

Through managing air pressure for braking systems and door operations, air compressors are indispensable to vehicle reliability and safety. Public transit systems rely heavily on them for daily operations which directly affects commuter satisfaction and efficiency of service. For instance, air compressors ensure trains maintain optimal speed and responsiveness, vital in high traffic networks. But what could this mean for future travel innovations?
Looking at air travel, compressors play a part in de-icing aircraft, protecting against dangerously low temperatures at high altitudes. Airlines require them for pressurization needs, improving in-flight comfort. As we explore deeper, the hidden mechanics reveal how substantial air compressors are to travel infrastructure, prompting us to reconsider their multifaceted impact. The revelations continue to inspire wonder.
The involvement of air compressors in automotive development is no less significant. They help achieve fast-paced assembly lines and maximize vehicle performance through efficient tire inflation systems. The dawn of electric transportation further amplifies their relevance, with ongoing research exploring integration with electric vehicle (EV) technology to build smarter, more sustainable transport methods. Prepare for insights that fundamentally change our perceptions.
From turbocharging businesses to invigorating economic activity, air compressors deliver cost savings and operational improvements that ripple across various sectors. Their capability to enhance workforce productivity and equipment longevity translates into reduced overheads and increased profit margins. However, their influence extends beyond mere economic metrics.

Small businesses benefit immensely from air compressors, as they enable cost-efficient scaling and diversification of service offerings. In manufacturing, they support automation that spurs economic growth by allowing smaller firms to compete with industry giants. By reducing time and resource demands, they democratize industrial capabilities, equipping local businesses with tools to expand effectively. The economic impact can be surprising!
In construction, air compressors drive vital tools such as jackhammers and pneumatic drills, enhancing project timelines and minimizing manual labor costs. Their deployment in agriculture, from powering irrigation systems to facilitating mechanized planting, underscores their value in maintaining sector vitality. These areas reveal a layers-deep narrative about how air compressors do more than power tools—they empower economies.
Even in finance, strategic adoption of compressor technology influences investment strategies and sector health forecasts. As enterprises seek innovative solutions in competitive landscapes, compressors often part of the conversation. Understanding these dynamics sheds light on evolving economic ecosystems and underscores the essential aid compressors offer toward sustainable growth. The directives below further illuminate these industrial synergies.
While air compressors have traditional applications, their role in fostering innovation is becoming increasingly evident. Through enabling 3D printing and supporting agile manufacturing, they catalyze novel production methods and advanced materials, reshaping modern industry practices. Those who harness these innovations find themselves at a strategic advantage.
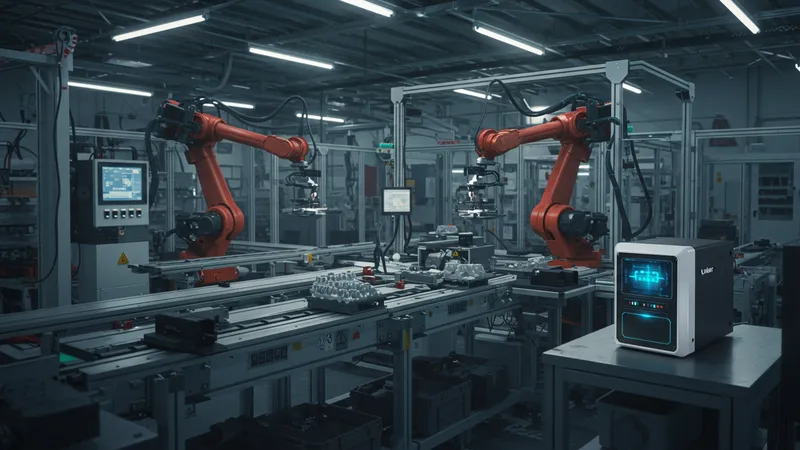

The marriage of air compressors with robotics reveals how they fuel the development of automata and intelligent machinery. This collaboration extends the frontier of what machinery can perform, offering versatility in previously unimaginable avenues. By propelling robotic limbs and advanced assembly lines, they are catalysts for futuristic tech reaching industries at large.
Turning to consumer products, compressed air powers the customization and personalization trend within manufacturing sectors. Companies can now tailor products en masse, satisfying niche consumer demands without sacrificing efficiency—a balance that fundamentally alters market dynamics. The story of compressors is just as much about thought-leadership as it is about tool utility.
As new technologies continue to emerge, the dynamic interfaces involving air compressors only expand. Whether it be in digital fabrication or nanotechnology, these tools aren’t just advancing; they are converging various tech disciplines to reinvent possibilities. In upcoming pages, we'll continue to demystify their transformative journey and unravel surprising tech synergies still left unheard.
Air compressors, while operating invisibly in many environments, are vital partners for countless unmet and unseen needs. In emergency services, they power rescue tools during critical times. This life-saving capability adds another dimension to their utility, as the dependable backbone for urgent and intricate operations.
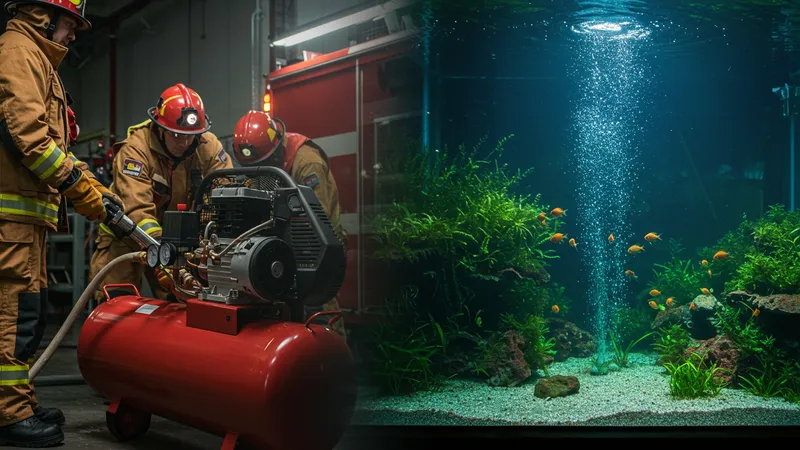

Beyond high-pressure scenarios, they are equally adaptive to calming tasks. For example, in aquaria, air compressors maintain ecosystem health by enabling water oxygenation. Their reliability ensures that aquatic life thrives, where their presence although silent, remains essential to sustainable aquarium environments.
For artists and creators, air compressors provide fine control over airbrush tools, essential for producing detailed artworks and customized designs. They are companions in exploring the fringes of creativity, supporting artwork from vast murals to intricate miniature models. There's an inherent magic in how they evoke potential without overshadowing artistry.
By exploring unexpected niches, air compressors surprise yet again in how they fulfill understated roles across diverse fields. When considered for stability and dependability, they inspire deeper insights into potential opportunities where creativity meets engineering excellence. Get ready to delve further into the orbit of their understated wonders.
As we peer into the future, the trajectory of air compressors aligns with tech advances and energy trends, indicating ever-evolving sophistication. Smart systems integrating IOT technology show how compressors will provide data-driven solutions that further enhance efficiency and predictive maintenance paradigms.
The advent of AI-infused compressors signals new horizons as these units learn and adapt usage patterns to optimize system performance. AI advances in predictive analytics will allow compressors to anticipate operational needs, reducing wear and increasing reliability, ultimately transforming how industries approach maintenance.
Furthermore, development in eco-conscious technologies for compressors means businesses can minimize their carbon footprints. Compressors supporting renewable energies will play a vital role in driving sustainable corporate growth, echoing industry demands for greener initiatives. This push toward sustainability reflects global conscientiousness about preserving our planet.
Alongside these advances, innovations continue to evolve, positioning compressors as key drivers in industrial modernization. The technological leaps ahead promise not only greater operational efficiencies but also limitless possibilities for applications we are yet to imagine. The journey toward this brave new world awaits discovery, full of revelations that will set the stage for future episodes!
Across hotels and resorts, air compressors discretely set standards for comfort and convenience. Whether through climate control systems or aiding maintenance operations, they play unexpected yet pivotal roles in defining guest experiences, often going unnoticed yet heavily relied upon.
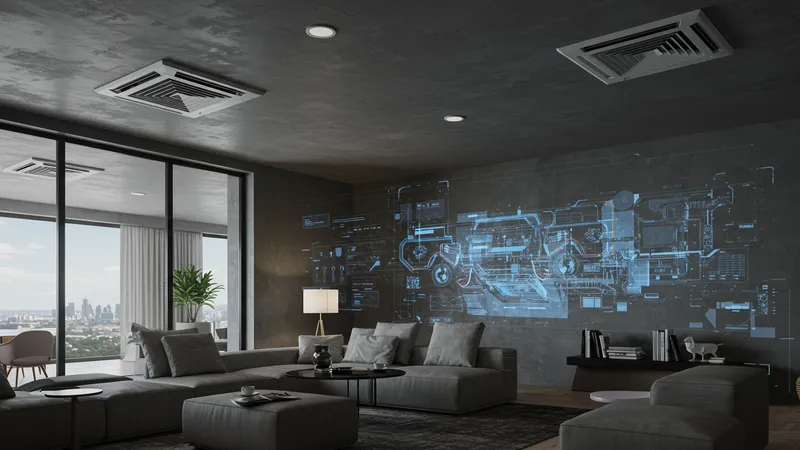

Coloring the unseen canvas of hospitality, they streamline service efficacy and ensure customer satisfaction by improving logistical processes. Smart compressor systems used in energy management not only reduce operational costs but enhance guest comfort through seamless heating, ventilation, and air conditioning solutions—an elixir for high-quality hospitality.
In addition to climate control, their utility extends to spa services, where compressors facilitate luscious steam baths and hydrotherapy treatments, crafting unforgettable guest moments. Such applications indicate their prowess in elevating service quality to unprecedented highs while maintaining operational feasibility.
The lesson here is clear: integrating air compressors in hospitality transforms typical experiences into memorable ones, offering fresh perspectives on upkeep and service delivery. Every detail in seamless service orchestration matters, and compressors are the hidden pillars making those seamless experiences possible. Revel in the unexpected intricacies that define modern hospitality's understated elegance.
When discussing usability and user-centric design, air compressors aren't the first tools to come to mind; however, they transform user experiences significantly in various settings. In the automotive sector, they enhance vehicle maintenance speed and efficiency, optimizing customer wait times and satisfaction.
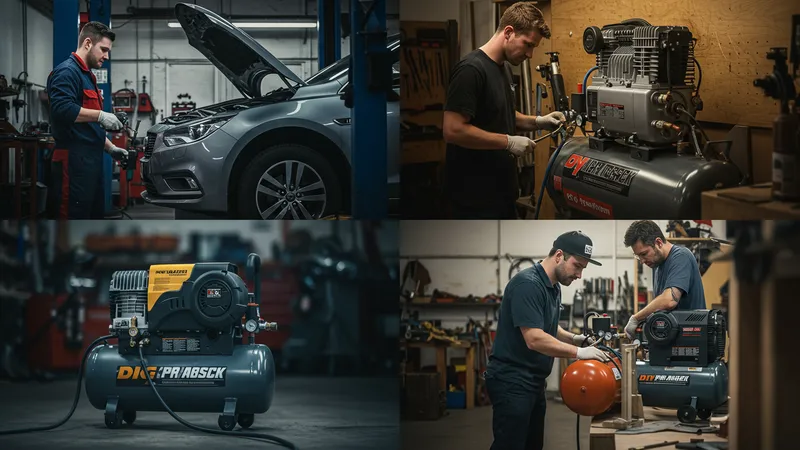

For personal skill development enthusiasts and DIY lovers, compressors offer a new dimension of capability, enabling capabilities that foster confidence in tackling more complex projects. They foster community amongst hobbyists by building experiential workmanship through reliable equipment that delivers consistent performance and flexes with user needs.
Businesses tapping into user engagement and satisfaction strategies find compressors’ quiet operation ideal for environments requiring minimal disruption, creating harmonious workspaces. This attribute significantly boosts environments like libraries, laboratories, and health centers aiming to maintain both functionality and ambiance.
Ultimately, air compressors illustrate how engineering sophistication elevates end-user interactions, providing enhancements that ripple outward to define positive user experiences across domains. Embrace the curious realm where compressors augment user satisfaction and reshape tool utility narratives. The circle completes as this realization powers an invaluable user-centric revolution.
In their most transformative element, air compressors act as critical players in energy management and optimization. Their role in harnessing and distributing compressed air efficiently addresses substantial energy cost reductions and framework improvements across sectors.
Effectively leveraging these tools allows factories to significantly lower their energy footprint, aligning operational methods with stringent regulatory standards and fostering greener practices. The efficiency benefits are substantial, with long-term savings offering lucrative incentives for energy-conscious enterprises.
Furthermore, applications in renewable energy systems spotlight how compressors bolster grid resiliency. They stabilize energy fluctuations, provide backup power, and enhance the consistency of energy supply—a facet seen in wind farms and hydroelectric plants relying on compressors for energy portability and stabilization.
As the demand for reliable, renewable energy sources grows, focusing on maximizing air compressor capabilities becomes pivotal. Collaborating with innovations in sustainable energy propels air compressors from mere functional devices to dynamic players actively solving global energy challenges. Witness how energy solutions come alive through an intersection of traditional technology and sustainable innovation.
Beyond technical prowess, air compressors influence broader cultural landscapes, shaping trends and public perception of technology's role in daily life. Their adaptability reflects universal themes of innovation, collaboration, and efficiency, showcasing the ubiquity of engineering marvels.
Cultural expressions that harness compressors’ latent capabilities include public art installations where themes of industrial beauty and power collide. In urban settings, they symbolize modernity and adaptability, becoming icons of technological advancement revered for their versatile applications.
The influence extends into education and storytelling media as compressors become focal tools of curiosity—resources that unravel the hidden layers of physics and mechanics. These stories inspire next-generation problem solvers and creators, inviting renewed appreciation for engineering wonders previously seen as mundane.
The lessons captured through air compressors emphasize the interconnectedness of science and society, unraveling narratives that showcase human ingenuity in surprising, creative forms. They are not just tools but instruments of cultural engagement and technological storytelling, bounded only by imagination. Unearth tales that highlight the profound cultural resonance of these unassuming devices.
The global traversal through air compressors’ many layers across industries and cultures redefines expectations of what such a versatile tool can achieve. As the narrative thickens, we gain insights about their remarkable ability to both sustain and innovate. In closing, air compressors are more than industry staples—they are lifelines boosting progress, carving greener futures, and echoing efficiency through time.
The exploration of their vertical and horizontal applications across domains reveals opportunities for strategic adoption that defy convention, fueling inspiration. It’s more than a narrative; it’s an ongoing journey of understanding and appreciation, setting the stage for future engagements with this humble yet impactful device. Share this eye-opening journey, bookmark for insights, and join the global dialogue celebrating the untapped potential of air compressors.