

Imagine a world where your face is your password, and identity theft becomes a relic of the past. Biometric scanners are not just science fiction anymore; they're transforming security at an unprecedented pace.
This technology is more crucial than ever, streamlining everything from airport check-ins to smartphone security, ensuring both convenience and heightened protection in today's digital age.

Biometric scanners come with unexpected capabilities. Beyond fingerprints, they analyze iris patterns and voice rhythms, providing multiple layers of identification. But that’s not even the wildest part—our physiology might hold the key to even faster and more accurate recognition systems.
Despite the promise of foolproof security, biometric scanners face significant privacy concerns. Some argue that centralized databases could be targeted for massive identity theft unlike any we've seen. But that’s not even the wildest part—find out how these systems could actually anticipate criminal behavior before it occurs.
What happens next shocked even the experts—an innovation that could redefine privacy, security, and our daily interactions with technology is waiting just ahead. Dive deeper to unravel the unfathomable surprises of biometric security.
While biometric systems are lauded for their elevated security, they are not without their vulnerabilities. A sophisticated cyber attack could potentially compromise the largest databases, leaving sensitive information susceptible to malicious misuse. Interestingly, while passwords can be changed, your fingerprint cannot, making the risk even higher. As researchers continue probing, they’ve exposed weaknesses that could have profound implications on privacy. But there’s one more twist—hackers have found ingenious ways to trick biometric systems using common household items.
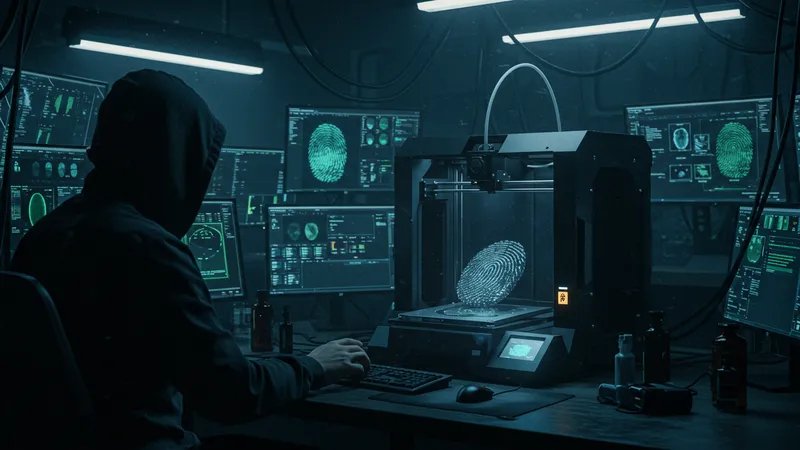

In a twist of irony, methods like 3D printing have been employed to manufacture fake fingerprints that can bypass sensors. This method, surprisingly, has been relatively successful but requires an unexpected level of skill and access to high-resolution images of a person’s fingerprint. Despite these revelations, biometric technology continues to be a popular choice for enhancing security. This paradox raises questions about whether convenience is being prioritized over safety.
Additionally, biometric systems bear the burden of high costs due to their need for specialized hardware and software. Even as the technology becomes more widespread, the financial overhead remains substantial for companies looking to integrate these systems. This expense is often passed on to consumers, hidden in service charges. This escalates the debate on the real cost versus the perceived benefits of biometric security systems.
Yet, there's a silver lining. With continuous research and improvements, especially in artificial intelligence, there are evolving defenses against these vulnerabilities. Anti-spoofing technologies are developing rapidly, aiming to create systems that learn and adapt over time, becoming almost contagious in their resilience. What you read next might change how you see this forever.
While primarily known for security, biometric scanners offer benefits that extend beyond mere identification. In healthcare, these systems can assist in patient record accuracy, reducing human error significantly. Elderly patients, who might forget their identification documents or struggle with password systems, benefit greatly from simple yet effective fingerprint or facial recognition systems. Surprisingly, this has led to a 30% decrease in medication administration errors in areas where such technology is implemented.
In education, biometric attendance systems are replacing traditional roll-calls. This innovation ensures that classroom time is maximized for learning rather than administrative tasks. Additionally, it provides a foolproof system discouraging truancy and boosting attendance rates significantly—by up to 25% in some institutions. These systems also alleviate teachers from mundane record-keeping, allowing them more focus on pedagogy.
Biometrics are also finding their way into hospitality, enhancing customer experiences. From personalized greetings upon hotel check-ins to room preference settings stored in personal profiles, guests are enjoying unprecedented levels of customization. Hotels have reported a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and loyalty following the implementation of these systems. This leap in the guest experience marks a new era in how services are rendered.
However, the most surprising benefit is yet to be fully realized. The integration of biometric systems with AI is poised to offer predictive analytics that could foresee and fulfill needs before they're expressed. Imagine a world where your preferences in dining, travel, or even entertainment are anticipated and effortlessly catered to. As fascinating as it all sounds, the underlying implications are worth exploring further.
The journey of biometric technology has been nothing short of revolutionary. Originally conceived as a futuristic concept, biometrics have evolved through significant milestones since their inception. Initially limited to fingerprint identification, the field has expanded to include diverse forms such as iris scanning, facial recognition, and even voice pattern analysis. These advancements have not only broadened scope but have also enhanced accuracy, diminishing error margins significantly. However, as sophisticated as these systems have become, they must continuously evolve to stay ahead of potential vulnerabilities.

Interestingly, the history of biometrics dates back to ancient times, with basic forms of personal identification found among civilizations through handprints. Today’s biometric systems are drastically more complex, yet they incorporate basic principles used centuries ago. With technology rapidly advancing, future systems may even incorporate behavioral biometrics, analyzing unique personal habits. The potential applications extend far beyond simple identification, offering dynamic security solutions that anticipate threats before they manifest.
Even more compelling is the democratization of biometric technology. What was once reserved for elite agencies and businesses due to prohibitive costs has gradually become mainstream. The increase in accessibility has been propelled by reduced production costs and amplified by consumer electronics integration, especially smartphones and smart home devices. This shift has prompted even small businesses to explore biometric solutions, ultimately contributing to a safer digital environment. However, this democratization raises important questions surrounding the ethical use of biometric data.
As the technology continues to progress, integrating biometrics with other cutting-edge technologies like blockchain is becoming a possibility. Such combinations could create impenetrable security networks that are both transparent and secure. Experts predict that the future of biometrics will not only redefine security but will also reshape societal norms around privacy and identity. But there’s another twist—what if biometrics could redefine trust in human interactions altogether?
Despite the convenience and security offered by biometric technology, there are mounting concerns about privacy. At the forefront of this debate is the sheer volume of personal data being collected and stored. With biometric identifiers being unique to each individual, any breach could lead to significant, irreversible privacy violations. Such considerations have industries reassessing how they store and secure biometric data, often resorting to high-grade encryption methods and decentralized databases to uphold data integrity.

Yet, the greatest challenge lies in finding a balance between improved security and individual freedom. The increasing adoption of biometric systems in public spaces underscores a concerning shift towards surveillance societies. In some countries, citizens fear that these technologies could be exploited for monitoring and control rather than their intended security purposes. Contrarily, some privacy advocates argue for tighter regulations and transparent policies to protect individuals from potential misuse.
Moreover, public perception plays a crucial role in the acceptance of biometrics. While many embrace them for the seamless experience they offer, others remain skeptical due to the lack of comprehensive data protections. Recent surveys have shown a rising skepticism towards sharing biometric information with corporations or governments, demanding stricter privacy standards. With privacy being a core societal value, the industry must navigate these complex waters carefully to maintain public trust.
However, there's an unexpected outcome: biometric systems could spearhead a new age of privacy-enhancing technologies rather than erode it. By fostering encrypted biometric data exchanges, individuals might regain control over their personal data security. This pivot, while fraught with challenges, hints at a future where privacy and security are not mutually exclusive but mutually reinforcing. As we delve deeper, the possibility of such systems revolutionizing data privacy emerges ever strongly.
As biometrics permeate our everyday lives, they continually press against legal and regulatory boundaries. Currently, the legislation surrounding biometrics varies widely across nations, with some adopting rigorous laws to protect individuals' biometric data while others are still grappling with the implications. In the U.S., for example, Illinois's Biometric Information Privacy Act represents one of the strictest and most comprehensive biometric protection laws.

Despite differing regulations, the common legal challenges include how to provide informed consent, manage data storage, and delineate clear usage policies. Businesses implementing biometric systems must navigate complex legal frameworks to ensure compliance, often requiring significant investments in legal expertise. These hurdles are further complicated by rapid technological advancements, which often outpace the creation and amendment of laws. This can leave gaps that could potentially jeopardize consumer protection.
The global adoption of biometrics has initiated international dialogues aimed at harmonizing regulations to establish universal biometric protection standards. Such efforts could significantly bridge the gap between rapid innovation and slow regulatory processes. However, achieving consensus remains a formidable task given the varied cultural and legal principles across regions. The challenge is magnified by threats of misuse, where lax laws could be exploited by entities with less ethical intentions.
Set against this backdrop, the legal evolution of biometric data protection unfolds. Forward-looking legal frameworks may incorporate biometric technologies as crucial components in enforcing rights. While challenges abound, this evolving landscape presents an opportunity for legal systems to align with technological progress, paving the way for innovation that prioritizes user security and trust. And yet, there’s more unbound potential to explore; redefining legal frameworks could potentially ensure justice and fairness in the digital realm, unlike ever before seen.
From unlocking your phone with a glance to seamlessly checking in at the airport, biometric technology has subtly woven itself into the fabric of daily life. With major tech companies continuously rolling out devices with advanced biometric capabilities, more people are experiencing the convenience firsthand. For instance, Face ID not only simplifies phone security but also enables secure financial transactions, making everyday tasks quicker and more efficient.

However, the impact of biometrics extends beyond consumer electronics. Workplaces are increasingly implementing biometric attendance and access systems, which streamline employee management and enhance facility security. While these systems optimize operations, they also raise questions about employee tracking and data privacy. Balancing efficiency with ethical considerations remains an ongoing debate.
In retail, personalized biometric experiences are gaining traction. Imagine walking into a store where your preferences and purchase history are recognized instantly, allowing for hyper-personalized recommendations and offers. Such convenience has the potential to revolutionize shopping, though it hinges on the consumer’s willingness to share personal data and the company’s ability to protect it. Transparency and trust are pivotal in encouraging widespread acceptance of these practices.
Fashion is another realm where biometrics are beginning to make waves. By understanding body metrics, brands can offer customized clothing and shoe fittings, reducing returns and enhancing customer satisfaction. This application highlights an exciting tangent, a future where technology truly understands individual needs. What transpires when these innovations expand further? The answer might redefine consumer-company interactions in profound ways.
Financial institutions are at the forefront of leveraging biometric technology to enhance security and streamline user experiences. With increasing incidents of cybercrime, banks are turning to biometric authentication to safeguard customer accounts. Fingerprint and facial recognition are being adopted for everything from secure access to mobile banking apps to verifying identities during transactions, providing a robust barrier against unauthorized access.

Moreover, the application of voice recognition in call centers for identity verification is not only enhancing security but reducing service time and improving customer satisfaction. This shift towards voice biometrics underscores a broader industry move to automate and enhance the user experience while maintaining stringent security protocols. However, the constant evolution of threats means that these technologies must continuously adapt to preempt attempts at breaching security.
In addition to security, biometrics offer financial institutions the potential for competitive differentiation. By delivering faster and more secure services, banks can improve their reputation and customer loyalty. For instance, biometric-based systems have been shown to significantly reduce fraud cases, instilling greater trust in consumers towards digital banking solutions. The adoption reflects a broader trend of embracing technology to address and solve modern security challenges.
Despite these benefits, the increased use of biometrics in finance brings privacy concerns to the forefront. Central to debates is ensuring that biometric data is protected in compliance with privacy laws and customer trust is uncompromised. Financial institutions face the challenge of balancing innovation with regulatory compliance, an undertaking that requires critical engagement with ethical, legal, and technological considerations. As we journey further, the role of biometrics in transforming financial landscapes beckons a closer look, promising both challenges and remarkable opportunities.
For years, travel security has been about long queues and extensive documentation checks, but biometrics are rapidly changing this narrative. Implemented in airports worldwide, biometric systems are enhancing travel security by streamlining passenger verification processes while minimizing human error. Biometric e-gates, which utilize face recognition technology, allow for efficient passenger flow, significantly reducing wait times during check-ins and border crossings.

This transformation elevates security by augmenting traditional methods with an additional layer of verification, reducing reliance on easily forged documents. Facial recognition technology has become a pivotal component, ensuring swift yet secure clearance. However, implementing such systems requires significant infrastructural investment and a careful balance between efficiency and privacy concerns, given the sensitivity of biometric data handling.
The convenience offered by biometrics extends beyond the check-in counter. Some airlines are exploring biometric boarding passes, intending to eliminate paper tickets completely. Travelers can proceed directly to their gate, cutting down pre-flight waiting time. As these innovations roll out, customer satisfaction levels are poised to rise, potentially redefining industry standards to become the norm in the coming years.
But biometrics offer more than just operational efficiency; they hold the promise of transforming customer experiences on a broader scale. As travel security systems continue to evolve, integration with other technologies like AI could offer predictive insights, anticipating potential threats before they occur. The implications are vast, potentially leading to an era of seamless, secure travel experiences worldwide.
Despite their many advantages, implementing biometric systems brings about unique challenges. One of the most significant is the cost associated with setup and maintenance. Installing cutting-edge biometric technology requires substantial investments in infrastructure and expert personnel to ensure systems are running smoothly and securely. This financial hurdle can be prohibitive, especially for smaller organizations.

Moreover, public skepticism over privacy and security concerns presents another barrier. Biometric systems deal with sensitive data, and any security breach could have severe repercussions. Thus, ensuring robust data protection measures and transparent privacy policies is critical to gaining user trust. Organizations must also navigate complex regulations that vary by region, ensuring compliance to avoid legal repercussions.
Interoperability challenges also arise due to the lack of standardized protocols. As various manufacturers develop biometric technologies independently, ensuring cohesive functionality across different systems becomes complicated. This inconsistency can lead to technical integration issues, requiring organizations to invest additional resources to achieve compatibility and ensure reliable performance.
Nevertheless, overcoming these challenges offers rewarding opportunities. Successfully addressing concerns and refining systems could lead to enhanced organizational efficiency and security. Moreover, as technology advances, the cost barriers are likely to decrease, making biometrics more accessible. This evolution presents an opportunity for early adopters to gain a competitive edge in security, convenience, and innovation.
The integration of biometrics with artificial intelligence represents a frontier of technological innovation, promising an enriched and seamless security experience. AI enhances biometric systems' accuracy by learning from large datasets and identifying subtle patterns uniquely associated with each individual. Such advanced functionality offers unprecedented verification precision, drastically reducing the potential for errors or fraudulent activities.

AI-powered biometric systems demonstrate remarkable adaptability. As they learn from continuous data inputs, they become adept at countering evolving security threats. By predicting and recognizing suspicious behaviors in real time, these systems bolster preventive security measures. Moreover, the collaboration between AI and biometrics paves the way for progressive developments that could revolutionize security solutions across various industries.
Incorporating AI not only refines but also expands the applications of biometrics. For instance, emotion recognition through AI-enhanced facial recognition opens possibilities in customer service and marketing, offering personalized experiences based on mood analysis. This cross-functional application highlights the transformative potential that lies in the convergence of these technologies, transcending traditional security uses.
Despite the promising synergy between AI and biometrics, challenges abound, notably concerning data privacy and ethics. Ensuring that AI systems operate fairly, without bias, is crucial to maintaining public trust. Emerging regulations are expected to establish guidelines that protect user data while encouraging innovation. As AI-driven biometric solutions continue to evolve, they herald a new era of intelligent, secure, and user-friendly systems. What you read next might forever alter your perception of how intertwined technology and human identity could become.
The horizon for biometric innovations is vast and filled with potential breakthroughs that promise to redefine our interactions with technology and security. Emerging technologies such as DNA-based biometrics hint at the next level of personal security—impossible to spoof and incredibly reliable. As research progresses, these cutting-edge systems could find applications in areas requiring high security, like government facilities and military operations.

Another exciting prospect lies in multi-modal biometric systems, which combine multiple biometric identifiers for enhanced security and accuracy. These systems use a combination of fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns, and voiceprints to provide a holistic security approach that is much harder to breach. This redundant security architecture addresses vulnerabilities present in single-modal systems, pointing towards a more robust security future.
As wearable technology becomes more advanced, integration with biometrics offers unprecedented convenience and personalization. Smart watches and fitness trackers could evolve to monitor biometric data not just for health metrics but also for seamless user device interaction. Such integration not only enhances convenience but promises a level of system interaction unachievable through traditional interfaces.
The future of biometrics beckons an era where technology blends seamlessly with our everyday existence, revolutionizing not just security but also how we access and control the digital world. As these innovations gradually take shape, they underscore the importance of ethical considerations and global standards to ensure a balanced approach to data privacy and security. With the continuous evolution of biometrics, the ultimate transformation in societal norms regarding security and personal identification is yet to unfold.
As biometric technology becomes increasingly prevalent, ethical considerations have come to the forefront of discussions. Central to these concerns is the question of consent: how organizations obtain, store, and use biometric data continues to evoke robust debate. Personal data control, ensuring individuals have the right to access, correct, or delete their data, is paramount, and businesses must navigate this complex ethical landscape to maintain trust.

The potential for bias in biometric systems further complicates ethical concerns. Algorithms trained on unrepresentative datasets can lead to inaccuracies that disproportionately affect certain demographics. Addressing these biases is crucial to developing fair and unbiased systems. Efforts are underway to refine algorithmic fairness and create inclusive datasets, promoting equitable biometric systems accessible to all.
Privacy and surveillance present another layer of ethical challenges. Biometrics, by design, are intended to improve security but could inadvertently lead to intrusive surveillance practices. Striking a balance between security and individual freedom is essential, prompting discussions around regulatory frameworks that protect against misuse while encouraging technological innovation.
Despite these hurdles, the prospect of biometrics enhancing privacy and security is promising. Transparent and accountable deployment of these technologies can engender confidence among users, fostering a positive relationship between technology and ethical principles. As we explore further, the path toward ethically aligned biometric systems could redefine the intersection of innovation, privacy, and trust.
As biometric technology continues to gain traction worldwide, its adoption reflects varying global trends driven by cultural, economic, and regulatory influences. In China, biometrics are deeply integrated into daily life, from facial recognition payment systems to public security and surveillance frameworks, making it a leader in widespread implementation. Conversely, the European Union has adopted a cautious approach, emphasizing stringent data privacy regulations to protect individual rights without stifling technological advancement.

In India, the Aadhaar program exemplifies large-scale biometric integration, offering identity management and enhancing public service delivery for over a billion citizens. This initiative highlights the transformative potential of biometrics in addressing societal challenges, including identity verification for governmental welfare schemes. However, it also raises questions about data security and privacy amidst vast information collection efforts.
In the United States, the focus is on leveraging biometric technology for security and convenience in sectors such as finance and travel. While public enthusiasm exists for the benefits offered by biometrics, the legislative landscape remains fragmented, presenting challenges in privacy regulation consistency. Efforts are underway to establish standardized frameworks that harmonize diverse approaches to data protection and privacy.
Globally, the push for biometric adoption continues to grow, balancing innovation with ethics and regulation. As more countries explore biometrics' potential to enhance security and streamline services, achieving a consensus on global standards remains integral to fostering trust and ensuring ethical deployment. The next chapter in this global narrative could redefine how nations leverage biometric technology to address both local and international challenges effectively.
Understanding who regulates biometric technologies is crucial to appreciating the complexities of this rapidly advancing field. On the international stage, no single governing body oversees biometric technology use, resulting in varied regulatory landscapes worldwide. This lack of uniformity can create challenges, particularly in cross-border applications where differing standards and policies may conflict.
In the United States, regulation is largely decentralized, with states enacting laws at their discretion. The Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) remains the benchmark, providing robust protections for biometric data. At the federal level, efforts to establish comprehensive laws have been ongoing, highlighting the necessity of a cohesive approach to address growing privacy concerns.
The European Union, with its General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), offers stringent rules on personal data, including biometrics, mandating explicit consent and transparency in data handling. Other nations are gradually adopting similar frameworks, acknowledging the significance of strong regulatory measures to protect civilian rights and maintain public trust.
As the global discourse on biometrics advances, developing coherent regulatory frameworks that transcend borders is imperative. These frameworks must balance the incredible potential of biometrics with essential protection of privacy and ethical integrity. The journey towards these integrated policies represents an opportunity to shape a future where biometric technology is safely and effectively harnessed for the greater good.
The journey through biometric technology is just beginning, offering an incredible fusion of promise and caution. The lessons learned from current implementations highlight the importance of striking a balance between innovation and ethics. As this field evolves, we stand at the cusp of a transformative shift that may define security and accessibility in profound ways.
Now, more than ever, it's vital to stay informed and engaged with how biometrics shape our world. Share this article to keep the discussion going and bookmark it for future updates, as the story of biometrics and their impact on our lives is only just unfolding.